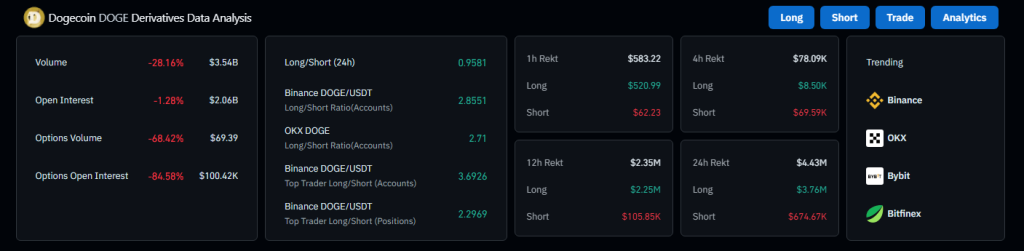
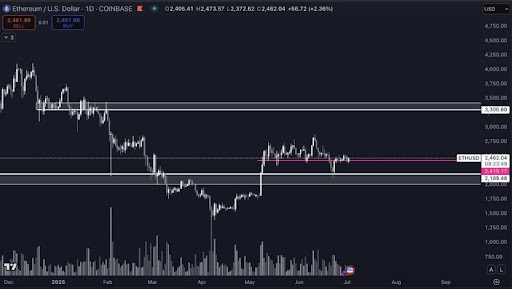
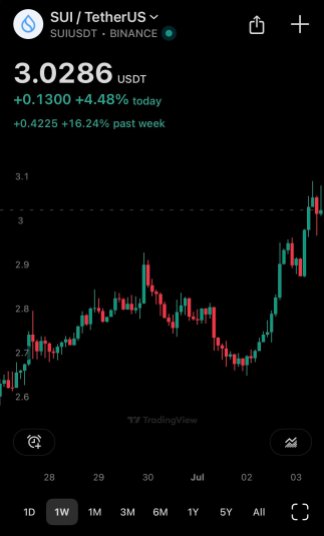
Introduction to Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency is a form of virtual or digital currency that uses cryptographic technology to secure financial transactions, control the creation of new units, and verify asset transfers. In contrast to traditional fiat currencies issued by central banks, cryptocurrencies run on decentralized networks such as blockchain, which are distributed across several computers or nodes.
Bitcoin, the most prominent and frequently used cryptocurrency, was founded in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group of individuals known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin pioneered the idea of a decentralized, peer-to-peer electronic currency system that allows users to conduct transactions directly without the necessity of intermediaries such as banks.
The Characteristics of Cryptocurrency
One of the fundamental characteristics of cryptocurrencies is their decentralization. They run on a computer network that collectively keeps a public record known as a blockchain. This ledger records all transactions and assures the data’s transparency, security, and immutability. Cryptocurrencies safeguard transactions and manage the generation of new units using cryptographic algorithms.
The Benefits of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies offer various advantages over traditional financial systems. They enable faster and more cost-effective cross-border transactions, as they are not bound by geographical boundaries or intermediaries. Furthermore, cryptocurrencies promote financial inclusion by enabling everyone with an internet connection to engage in the global economy, regardless of location or access to traditional banking services.
Furthermore, cryptocurrencies provide people with more control over their financial holdings. Cryptocurrencies are often stored in digital wallets containing public and private keys. Private keys are used to access and maintain Bitcoin assets, whereas public keys are used to receive cash. Individuals now have complete ownership and control over their funds, avoiding the possibility of censorship or seizing by third parties.
Cryptocurrencies have also paved the path for innovation across various businesses. They’ve made it possible to create decentralized apps (DApps) and smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined conditions encoded into code. These technologies have enabled decentralized financing (DeFi), asset tokenization, and the development of unique digital assets known as non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
A Note: However, it’s important to note that the cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and speculative. Prices can change significantly, and investing in cryptocurrency is speculative. Cryptocurrency regulatory regimes vary among jurisdictions. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the legal and tax implications in your nation before engaging in cryptocurrency operations.
The Top 14 Commonly Used Terms in the World of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency:
A digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets.
Blockchain:
A decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions across multiple computers or nodes. It ensures transparency, security, and immutability of the data.
Digital Wallet:
A digital application or device used to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. It contains public and private keys necessary for accessing and managing cryptocurrency holdings.
Bitcoin:
The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created by an anonymous person or group of people known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a decentralized network and serves as a digital store of value and a medium of exchange.
Altcoin:
Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Altcoin is a broad term that encompasses all cryptocurrencies besides Bitcoin, such as Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, and more.
ICO (Initial Coin Offering):
A fundraising method in which a new cryptocurrency project sells its tokens in exchange for established cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum. It helps startups raise capital for their projects.
Mining:
The process of verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain, typically performed by specialized computers or mining rigs. Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrencies.
Smart Contract:
Self-executing contracts with predefined conditions written into code on a blockchain. Smart contracts automatically facilitate and enforce the terms of the agreement, removing the need for intermediaries.
Decentralization:
The distribution of control and authority across a network of computers or nodes rather than relying on a central authority. Decentralization is a fundamental principle in cryptocurrencies, aiming to eliminate single points of failure and enhance security.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance):
Refers to a financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology that aims to provide traditional financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without the need for intermediaries like banks. DeFi platforms typically utilize smart contracts.
NFT (Non-Fungible Token):
A type of cryptographic token representing a unique digital asset or item, such as artwork, music, videos, or virtual real estate. Unlike cryptocurrencies, NFTs are indivisible and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis due to their uniqueness.
Stablecoin:
A type of cryptocurrency designed to minimize price volatility by pegging its value to a stable asset like fiat currency (e.g., US Dollar) or commodities (e.g., gold). Stablecoins offer a more reliable unit of account and can be useful for trading and storing value.
Yield Farming:
A practice in DeFi where investors provide liquidity to decentralized protocols in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens. Yield farmers lock up their cryptocurrencies in smart contracts to earn interest or other incentives.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization):
An organization governed by smart contracts and operated by its members or token holders. DAOs aim to achieve decentralization by allowing participants to vote on proposals, make decisions collectively, and manage resources without a centralized authority.
These terms reflect some of the latest developments and trends in the cryptocurrency space. It’s always beneficial to stay informed and explore further to understand the nuances of these concepts fully.